We think of our Liver as the MAIN DETOXIFICATION ORGAN. Yes, true. It actually has hundreds of functions including storage of vitamins and minerals, producing and mitigating cholesterol, breaking down fat, making triglycerides, regulating blood sugar, and metabolizing amino acids.
What is detoxification? The liver is responsible for transforming and clearing toxic substances from the blood. “Toxic products” refers to anything from microorganisms, contaminants, drugs, alcohol, pesticides, and our own metabolic end products.
In our modern environment, we are exposed to toxins every day. Sometimes it is these external sources (medications, pesticides, chemicals, etc). But, the majority of toxins we deal with are a normal byproduct of our internal processes.
Regardless of where they come from, our liver processes these toxins in the same way to ‘neutralize’ and eliminate them: a concept we know as DETOXIFICATION.

Phase I Detox
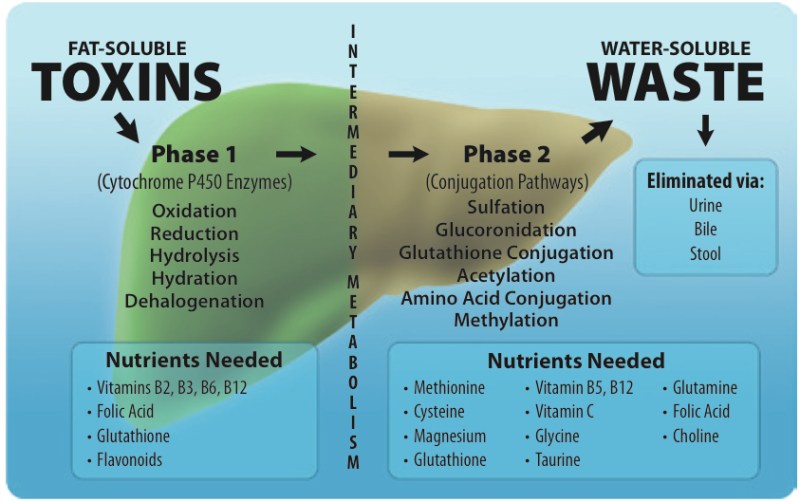
Detoxification happens in two phases. The first phase (PHASE I) is a biotransformation reaction facilitated by a specific class of enzymes called Cytochrome P450. Through oxidation, reduction, and hydrolysis reactions toxins are converted into more water-soluble compounds.
Often, Phase I biotransformation creates even more reactive species and an increase of free radicals in the body. We rely on antioxidants during the intermediary stage to ensure our cells are protected.
Nutrient deficiencies, heavy metals, liver damage, and some drugs can impair the CYP450 enzymes, slowing down Phase I detoxification.
Phase II Detox
In Phase II detoxification we conjugate the now transformed toxins into a fully water-soluble compound that can be excreted. The biggest four pathways of conjugation are: glutathionation, glucoronidation, sulfation, and glycination. Amino acids (or sulfur) are added to the already partially transformed toxins to “neutralize” them.
Protein is vitally important to complete this phase (as that’s where we get these Amino acid co-factors). When Phase II is impaired, it can result in a ‘backup’ of fat-soluble toxins that get stored in our fatty tissue. Poor Phase II detoxification can mean hormone imbalances, recurrent infections, headaches, chemical sensitivities, and more.
Phase III Detox
While not an official phase of detoxification, Phase III is the final excretion of the fully water soluble compounds. They are transported from the liver to the intestines where they can bind with bile (and fiber!!) and excreted via the feces [or the kidney to be excreted through urine].
If you’re constipated, or dehydrated, you are NOT detoxifying well.
Optimal Liver Detoxification – Diet and Beyond
Clearing Up Misconceptions
The liver is more like a filter than a sponge. It doesn’t absorb toxins and it doesn’t STORE toxins (that happens in fatty tissue). Instead, the liver stores important nutrients like Vitamins A, D, E, and K, Vitamin B12; minerals like iron, copper; and many of the cofactors required for the detoxification process. See why Liver is a SUPERFOOD?!
Ensuring Optimal “DETOX”
No, you don’t need to go on a juice fast to detox. In fact, when you are consuming only juices or ‘detox’ teas I would argue you’re putting yourself in a MORE reactive state since you aren’t providing the necessary amino acids to complete the conjugation. Further, when you are not consuming enough fiber, you will recirculate end products instead of eliminating them from the body!

So, what ARE the best foods and nutrients to support Liver Detox?
For Phase I, we need a number of vitamins and minerals to support the CYP450 enzymes. This includes manganese, Vitamin A, Vitamin B2, B3, B5, B6, B12, and folate. Antioxidants like Vitamin C, Vitamin E, Beta Carotene, Zinc, and Selenium are also important for handling the free radicals produced.
For Phase II, we need the building blocks to attach to the transformed toxins. This includes glutamine, cysteine, methionine, and taurine.
Glutathione is the “master antioxidant” because it plays a role in both Phase I and Phase II detoxification!
The best diet for supporting optimal detoxification is one filled with a variety of colorful plants, nutrient-dense animal proteins, and adequate fiber. If you’re following a vegetarian (or carnivore) diet, you’ll need to be especially cognizant to include essential amino acids!
Want a free resource for increasing PHYTONUTRIENTS in your diet and supporting Liver Detoxification?
Click here to get the Phytonutrient Spectrum Guide by the IFM curated by Dr. Deanna Minich.

Want to work with a functional nutritionist to personalize your diet? Struggling with hormone imbalance, IBS, weight gain, mood changes? Let’s look at FOOD FIRST. Read more about Functional Nutrition at The Facility here.
Click here to schedule a free 15 minute phone consult with Kate!






One Response